To use with CircuitPython, you need to first install a few libraries, into the lib folder on your CIRCUITPY drive. Then you need to update code.py with the example script.
Thankfully, we can do this in one go. In the example below, click the Download Project Bundle button below to download the necessary libraries and the code.py file in a zip file. Extract the contents of the zip file, open the directory CPB_Magic_Light_Mixer/ and then click on the directory that matches the version of CircuitPython you're using and copy the contents of that directory to your CIRCUITPY drive.
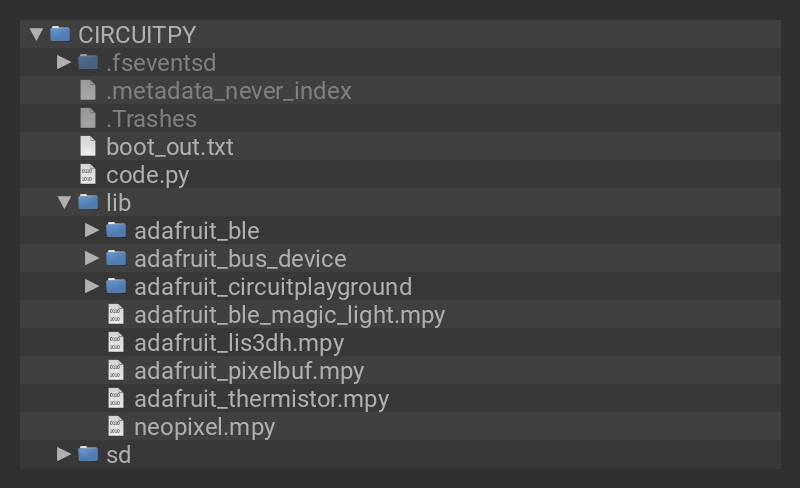
Your CIRCUITPY drive should now look similar to the following image:
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2020 John Edgar Park for Adafruit Industries
#
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
# Magic Light Bulb remote color mixer
# Sends RGB color values, read from three faders on CPB to the bulb
# https://www.magiclightbulbs.com/collections/bluetooth-bulbs
import adafruit_ble
from adafruit_ble.advertising.standard import ProvideServicesAdvertisement
from adafruit_ble_magic_light import MagicLightService
import _bleio
import board
from analogio import AnalogIn
from adafruit_circuitplayground import cp
def find_connection():
for connection in radio.connections:
if MagicLightService not in connection: # Filter services
continue
return connection, connection[MagicLightService]
return None, None
radio = adafruit_ble.BLERadio()
def scale(value):
# Scale a value from 0-65535 (AnalogIn range) to 0-255 (RGB range)
return int(value / 65535 * 255)
a4 = AnalogIn(board.A4) # red slider
a5 = AnalogIn(board.A5) # green slider
a6 = AnalogIn(board.A6) # blue slider
cp.pixels.brightness = 0.1
dimmer = 1.0
active_connection, bulb = find_connection() # In case already connected
while True:
if not active_connection: # There's no connection, so let's scan for one
cp.pixels[0] = (60, 40, 0) # set CPB NeoPixel 0 to yellow while searching
print("Scanning for Magic Light...")
# Scan and filter for advertisements with ProvideServicesAdvertiesment type
for advertisement in radio.start_scan(ProvideServicesAdvertisement):
# Filter further for advertisements with MagicLightService
if MagicLightService in advertisement.services:
active_connection = radio.connect(advertisement)
print("Connected to Magic Light")
cp.pixels[0] = (0, 0, 255) # Set NeoPixel 0 to blue when connected
# Play a happy tone
cp.play_tone(440, 0.1)
cp.play_tone(880, 0.1)
print("Adjust slide potentiometers to mix RGB colors")
try:
bulb = active_connection[MagicLightService]
except _bleio.ConnectionError:
print("disconnected")
continue
break
radio.stop_scan() # Now that we're connected, stop scanning
while active_connection.connected: # Connected, now we can set attrs to change colors
# Toggle slide switch to go to half or full brightness
if cp.switch:
cp.red_led = True
dimmer = 0.5
else:
cp.red_led = False
dimmer = 1.0
# Press the 'A' button to momentarily black the bulb
if cp.button_a:
dimmer = 0.0
r = scale(a4.value * dimmer)
g = scale(a5.value * dimmer)
b = scale(a6.value * dimmer)
# Press the 'B' button to momentarily white the bulb
if cp.button_b:
r, g, b = (255, 255, 255)
color = (r, g, b)
try:
bulb[0] = color # Send color to bulb's color characteristic
except _bleio.ConnectionError:
print("disconnected")
continue
cp.pixels[2] = (r, 0, 0)
cp.pixels[3] = (0, g, 0)
cp.pixels[4] = (0, 0, b)
cp.pixels[7] = (color)
active_connection = None # Not connected, start scanning again
cp.pixels[0] = (60, 40, 0)
How it Works
Libraries
First, the code imports the libraries necessary for using Bluetooth LE (adafruit_ble, _bleio) and the more specialized adafruit_ble_magic_light library to deal with the specifics of this profile.
We also import adafruit_ble.advertising.standard ProvideServicesAdvertisement so we can do some filtering of the Peripheral advertisements being broadcast by myriad devices and hone in on the ones we want.
Additionally, we import board, analogio AnalogIn, and adafruit_circuitplayground so we can use the sliders, buttons, slide switch, on-board NeoPixels, and speaker on the CPB with simple, high level commands.
import adafruit_ble from adafruit_ble.advertising.standard import ProvideServicesAdvertisement from adafruit_ble_magic_light import MagicLightService import _bleio import board from analogio import AnalogIn from adafruit_circuitplayground import cp
Find Connection
Next we'll define a function called find_connection() that we'll use later to search through available Peripheral connections for only the one that offers the MagicLightService.
def find_connection():
for connection in radio.connections:
if MagicLightService not in connection: # Filter services
continue
return connection, connection[MagicLightService]
return None, None
Instantiate Radio
We instantiate the Bluefruit LE radio with this command:
radio = adafruit_ble.BLERadio()
Analog Read Setup
To use the slide potentiometers we'll need to define a function called scale(value) that can convert the raw analog voltage readings to a 0-255 range that's used per RGB color value.
We'll also define the analog pin read variables for the CPB's A4, A5, and A6 pads.
def scale(value):
# Scale a value from 0-65535 (AnalogIn range) to 0-255 (RGB range)
return int(value / 65535 * 255)
a4 = AnalogIn(board.A4) # red slider
a5 = AnalogIn(board.A5) # green slider
a6 = AnalogIn(board.A6) # blue slider
Next, we'll set the on-board NeoPixel brightness using the cp.pixels.brightness = 0.1 command.
We'll also create a variable called dimmer and set it to a value of 1.0 -- this will be used as a multiplier for the color values and will be changed to 0.5 when the slide switch is engaged.
Main Loop
During the main loop of the program, we check to see if there's an active connection, and if not we set the first CPB NeoPixel to yellow.
We then begin scanning through the filtered advertisements for the MagicLightService that's being broadcast by the bulb.
If the bulb is found, a connection is made and the CPB's first pixel is set to blue, and a happy tone is played, and the radio stops scanning for connections.
while True:
if not active_connection: # There's no connection, so let's scan for one
cp.pixels[0] = (60, 40, 0) # set CPB NeoPixel 0 to yellow while searching
print("Scanning for Magic Light...")
# Scan and filter for advertisements with ProvideServicesAdvertiesment type
for advertisement in radio.start_scan(ProvideServicesAdvertisement):
# Filter further for advertisements with MagicLightService
if MagicLightService in advertisement.services:
active_connection = radio.connect(advertisement)
print("Connected to Magic Light")
cp.pixels[0] = (0, 0, 255) # Set NeoPixel 0 to blue when connected
# Play a happy tone
cp.play_tone(440, 0.1)
cp.play_tone(880, 0.1)
print("Adjust slide potentiometers to mix RGB colors")
try:
bulb = active_connection[MagicLightService]
except _bleio.ConnectionError:
print("disconnected")
continue
break
radio.stop_scan() # Now that we're connected, stop scanning
Connected
Once the connection has been made, we check the CPB slide switch to set half or full brightness, and also flip the on board red_led on or off respectively to indicate dim/full mode.
We check for the CPB A button press and set the dimmer value to 0.0 if pressed.
The r, g, b variables are adjusted according to the scaled analog readings of the slide potentiometers, and multiplied by the dimmer variable value.
We check for the CPB B button press and set the r, g, b values to 255, 255, 255 if pressed.
Now, we create a color variable and cast the current r, g, b values to it, so we can send these values to the bulb.
while active_connection.connected: # Connected, now we can set attrs to change colors
# Toggle slide switch to go to half or full brightness
if cp.switch:
cp.red_led = True
dimmer = 0.5
else:
cp.red_led = False
dimmer = 1.0
# Press the 'A' button to momentarily black the bulb
if cp.button_a:
dimmer = 0.0
r = scale(a4.value * dimmer)
g = scale(a5.value * dimmer)
b = scale(a6.value * dimmer)
# Press the 'B' button to momentarily white the bulb
if cp.button_b:
r, g, b = (255, 255, 255)
color = (r, g, b)
try:
bulb[0] = color # Send color to bulb's color characteristic
except _bleio.ConnectionError:
print("disconnected")
continue
Feedback
Since we've got spare pixels on the CPB, why not use them for some user feedback?! We'll set pixels 2, 3, and 4 to the pure red, green, and blue levels and then set pixel 7 to the combined color value, the same as the bulb.
cp.pixels[2] = (r, 0, 0) cp.pixels[3] = (0, g, 0) cp.pixels[4] = (0, 0, b) cp.pixels[7] = (color)
Next we'll assemble the parts to use our color mixer!


















