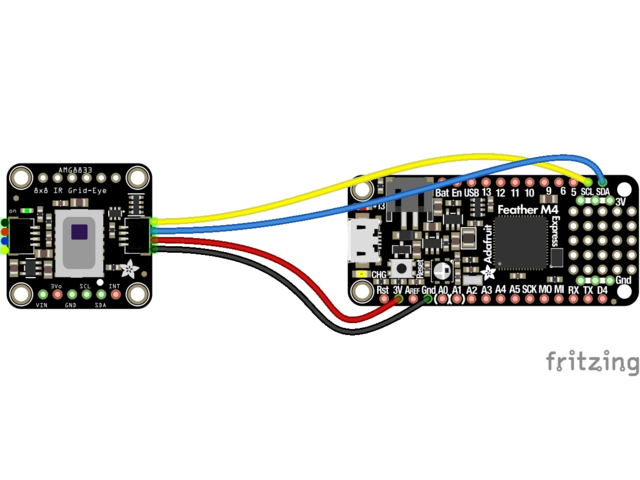
It's easy to use the AMG8833 sensor with Python or CircuitPython and the Adafruit CircuitPython AMG88xx module. This module allows you to easily write Python code that reads thermal imaging data from the sensor.
You can use this sensor with any CircuitPython microcontroller board or with a computer that has GPIO and Python thanks to Adafruit_Blinka, our CircuitPython-for-Python compatibility library.
CircuitPython Microcontroller Wiring
First wire up a AMG8833 to your board exactly as shown on the previous pages for Arduino. Here's an example of wiring a Feather M0 to the sensor with I2C:
-
Board 3V to sensor VIN (red wire on STEMMA QT version)
-
Board GND to sensor GND (black wire on STEMMA QT version)
-
Board SCL to sensor SCL (yellow wire on STEMMA QT version)
-
Board SDA to sensor SDA (blue wire on STEMMA QT version)
Python Computer Wiring
Since there's dozens of Linux computers/boards you can use we will show wiring for Raspberry Pi. For other platforms, please visit the guide for CircuitPython on Linux to see whether your platform is supported.
Here's the Raspberry Pi wired with I2C:
-
Pi 3V3 to sensor VIN (red wire on STEMMA QT version)
-
Pi GND to sensor GND (black wire on STEMMA QT version)
-
Pi SCL to sensor SCL (yellow wire on STEMMA QT version)
-
Pi SDA to sensor SDA (blue wire on STEMMA QT version)
CircuitPython Installation of AMG88xx Library
You'll need to install the Adafruit CircuitPython AMG88xx library on your CircuitPython board.
First make sure you are running the latest version of Adafruit CircuitPython for your board.
Next you'll need to install the necessary libraries to use the hardware--carefully follow the steps to find and install these libraries from Adafruit's CircuitPython library bundle. Our CircuitPython starter guide has a great page on how to install the library bundle.
For non-express boards like the Trinket M0 or Gemma M0, you'll need to manually install the necessary libraries from the bundle:
- adafruit_amg88xx.mpy
- adafruit_bus_device
Before continuing make sure your board's lib folder or root filesystem has the adafruit_amg88xx.mpy, and adafruit_bus_device files and folders copied over.
Next connect to the board's serial REPL so you are at the CircuitPython >>> prompt.
Python Installation of AMG88xx Library
You'll need to install the Adafruit_Blinka library that provides the CircuitPython support in Python. This may also require enabling I2C on your platform and verifying you are running Python 3. Since each platform is a little different, and Linux changes often, please visit the CircuitPython on Linux guide to get your computer ready!
Once that's done, from your command line run the following command:
sudo pip3 install adafruit-circuitpython-amg88xx
If your default Python is version 3 you may need to run 'pip' instead. Just make sure you aren't trying to use CircuitPython on Python 2.x, it isn't supported!
CircuitPython & Python Usage
To demonstrate the usage of the sensor we'll initialize it and read the thermal imaging data the board's Python REPL.
If you're using an I2C connection run the following code to import the necessary modules and initialize the I2C connection with the sensor:
import time import busio import board import adafruit_amg88xx i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA) amg = adafruit_amg88xx.AMG88XX(i2c)
Now you're ready to read values from the sensor using any of these properties:
- temperature - The sensor temperature in degrees Celsius.
- pixels - Temperature of each pixel across the sensor in Celsius. Temperatures are stored in a two dimensional list where the first index is the row and the second is the column. The first row is on the side closest to the writing on the sensor.
For example, to print the pixel temp once every second until you tell it to stop:
while True:
for row in amg.pixels:
print(['{0:.1f}'.format(temp) for temp in row])
print("")
print("\n")
time.sleep(1)
That's all there is to using AMG88ss with CircuitPython!
# SPDX-FileCopyrightText: 2021 ladyada for Adafruit Industries
# SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
import time
import busio
import board
import adafruit_amg88xx
i2c = busio.I2C(board.SCL, board.SDA)
amg = adafruit_amg88xx.AMG88XX(i2c)
while True:
for row in amg.pixels:
# Pad to 1 decimal place
print(["{0:.1f}".format(temp) for temp in row])
print("")
print("\n")
time.sleep(1)